© Nepal Geotechnical Society


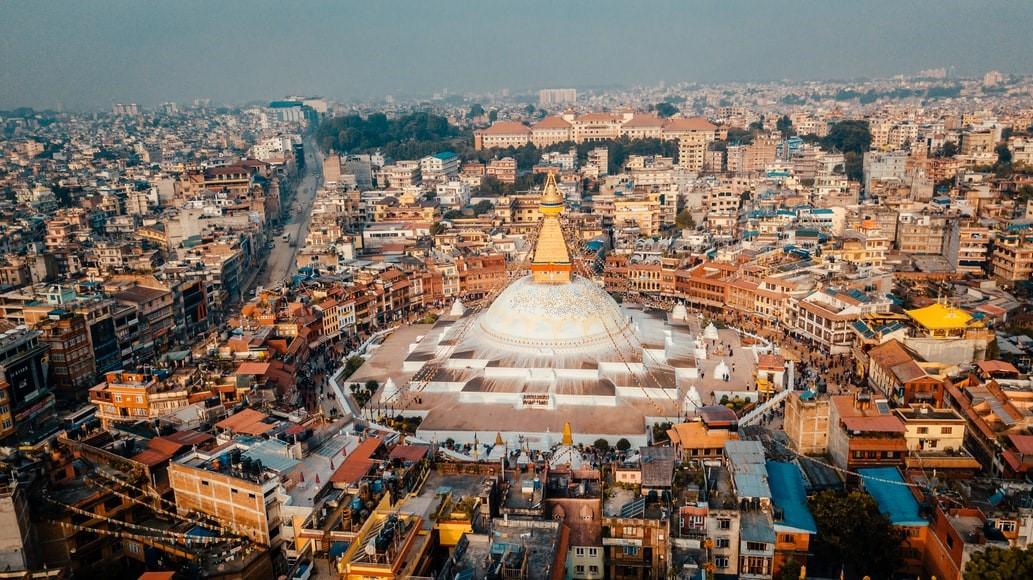
The conference will be held in Kathmandu (in Nepali- काठमाडौँ and also spelled Katmandu or Kantipur), the capital city of Nepal. With an estimated population of about four million, the city of Kathmandu is the biggest and an important historic urban settlement in Nepal. In its neighborhood are two more ancient cities of Nepal; Lalitpur and Bhaktapur, which altogether make up the capital area of the nation. All three cities have historically important cultural monuments that attract about a million international and domestic tourists every year. Both as the administrative and cultural capital of Nepal, the Kathmandu Valley encompassing three major and two minor urban settlements and several rural settlements accommodates nearly 16% of the nation’s population. At an average altitude of 1350 meters, the Kathmandu Valley ground is ancient lake sediment that at its deepest point measures about 500 meters. Once thought to be the fabled and inaccessible Shangri-La, Kathmandu is now a hub for independent travelers as well as a growing vacation spot catering to all budgets. You will enjoy clear, blue sky and white mountains from any famous sites, of which it has many: a whopping seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites within a few miles!
The city was established in the 2nd century CE, making it one of the world’s longest continually inhabited cities. The Newar people, a cosmopolitan urban civilization in the Himalayan foothills, have made this valley, once known as the “Nepal Mandala,” their home for centuries. The city was the seat of the Nepalese monarchy and was filled with the palaces, homes, and gardens of the country’s elite.
Kathmandu is also the cultural, artistic, and economic hub of Nepal. The majority of its diverse population practices Hinduism or Buddhism. The inhabitants of Kathmandu place a high value on religious and cultural celebrations. The city relies heavily on tourism, which contributes significantly to the local economy. Kathmandu, Nepal was named TripAdvisor’s No. 1 upcoming destination in Asia and No. 3 worldwide in 2013.

To know more about the city, please visit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kathmandu#Kathmandu_administration; https://wikitravel.org/en/Kathmandu
To see the majestic glimpses of the Kathmandu Valley please visit https://www.holidify.com/places/kathmandu/photos.html
To experience a drone-captured bird’s eye view of the Kathmandu Valley in 4K quality please click the link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cjIFMuNZufY
Visa can be obtained on arrival at the Tribhuvan International Airport, Kathmandu, at border entry points in Kakadvitta, Birgunj, Bhairahawa, Nepalgunj, Gaddachowki on the Nepal-India border, and Kodari on the Nepal-China border. Visa can also be obtained at the nearest Nepal Embassy or Diplomatic Mission. Visa can also be obtained (for renewal purposes) at the Department of Immigration, Kalikasthan, Kathmandu. A valid passport and one passport-size photo with a light background are required. Immigration Department has not specified the size of the passport size photo.
Visa can be obtained only through payment of cash in the following currency: Euro, Swiss Franc, Pound Sterling, US Dollar, Australian Dollar, Canadian Dollar, Hong Kong Dollar, Singapore Dollar, and Japanese Yen. Credit cards, Indian currency, and Nepali currency are not accepted as payment of visa fees.
Visa Facility Duration Fee
Multiple entry 15 days US$ 25 or equivalent convertible currency
Multiple entry 30 days US$ 40 or equivalent convertible currency
Multiple entry 90 days US$ 100 or equivalent convertible currency
For the first visit in one visa year (January to December), a gratis visa for 30 days is available only for nationals of South Asian countries like Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. However, the visa can be extended from the Immigration Department on payment of the visa fee as specified above.
Indian nationals do not require a visa to enter Nepal. As per the Nepalese Immigration, Indian Nationals traveling to Nepal must possess one of the following documents:
Passport, Driving License with photo, Photo Identity card issued by a Government Agency, Ration Card with Photo, Election Commission Card with Photo, Identity Card issued by the Embassy of India in Kathmandu, Identity Card with Photo issued by a Sub-Divisional Magistrate or any other officials above his/her rank.
Also, please check with your nearest travel agents for documents required by Indian Immigration for Indians traveling to Nepal.
Nationals from Nigeria, Ghana, Zimbabwe, Swaziland, Cameroon, Somalia, Liberia, Ethiopia, Iraq, Palestine, and Afghanistan will need to obtain a visa from Nepalese Embassies or Diplomatic Missions in their respective countries, as they do not get a visa upon arrival at the immigration entry points of Nepal.
Tourists can stay for a maximum of 150 days in a visa year (Jan 1 to Dec 31).
For further information, please contact: the Department of Immigration, Kalikasthan, Kathmandu, Nepal (Email: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]) [Source: Ministry of Culture, Tourism and Civil Aviation]
Kathmandu Valley is in the Warm Temperate Zone of Nepal (elevation ranging from 1,200–2,300 meters (3,900–7,500 ft)), where the climate is fairly temperate, atypical for the region. This zone is followed by the Cool Temperate Zone with elevation varying between 2,100–3,300 meters (6,900–10,800 ft). Portions of the city with lower elevations have a humid subtropical climate, while portions of the city with higher elevations generally have a subtropical highland climate. The city generally has a climate with warm days followed by cool nights and mornings. Rainfall is mostly monsoon-based. Rainfall has been recorded at about 1,400 millimeters (55.1 in) for the Kathmandu valley, and averages 1,407 millimeters (55.4 in) for the city of Kathmandu. On average humidity is 75%.
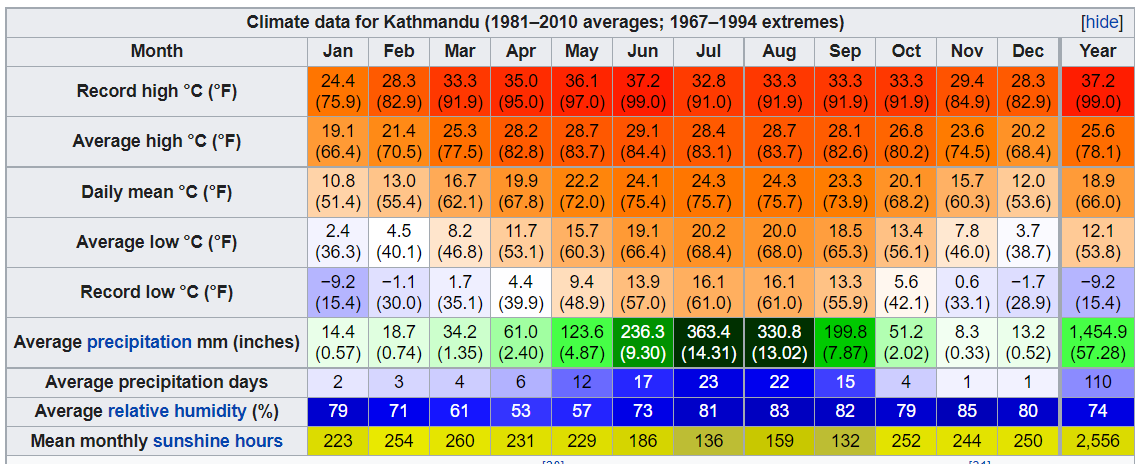
Fig: Climate data for Kathmandu (Source: www.wikipedia.org)
For up-to-date weather reports please click on the following link: https://www.timeanddate.com/weather/nepal/kathmandu
The monetary unit in Kathmandu (Nepal) is Nepalese Rupees (NPR or NRs or Rs).
The current rate of normal Value Added Tax (VAT) in Nepal is 13%.
The accepted cards are Visa, Master Card, Maestro, Diners Card, Cirrus, and American Express. If you want to pay using your credit card, there is a service charge of 3.5%.
your credit/debit cards to withdraw money from the numerous Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) if you don’t like carrying a lot of cash. Some of you are fortunate that your bank back home reimburses you the fee local banks charge you for dispensing your money. Sometimes, the machines might not be working. Still, as mentioned above, many ATMs in major cities accept International cards, dispatching cash in Nepalese rupees. There is a security guard outside the ATM lounge or machine.
This doesn’t happen often, but it is better to use ATM outside its related bank just if the machine retains your card so you can retrieve it from the bank.
Payments in hotels, travel agencies, and airlines are made in foreign exchange. Credit cards like American Express, Master, and Visa are accepted at major hotels, shops, and restaurants. Remember to keep your foreign exchange encashment receipt while making foreign exchange payments or transferring foreign currency into Nepali rupees. The receipts may be needed to change left-over Nepali currency into hard currency before leaving the country. However, only 10 percent of the total amount may be converted by the bank. ATM is widely in use in Kathmandu.
Major banks, hotels, and exchange counters at Tribhuvan International Airport (Kathmandu) provide services for exchanging foreign currency. Exchange rates are published in English dailies such as The Rising Nepal, The Kathmandu Post, and The Himalayan Times. Nepali currency notes are found in denominations of Rupees 1000, 500, 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 2, and 1 while coins are found in denominations of Rupees 5, 2, and 1. One rupee equals 100 paisa.
Time Zone of Nepal, GMT + 5:45 hours
Nepali is the official, national language and serves as lingua franca among Nepalis of different ethnolinguistic groups. Hindi – along with regional dialects Awadhi, Bhojpuri, and Maithili – are spoken in the southern Terai Region. Hindi is also widely understood by Nepalis who have worked, studied or traveled in India. Many Nepali in government and business speak English as well. In the capital Kathmandu, Nepali, Nepal Bhasa (the Newar language), and English are the most widely understood languages.
Kathmandu is a great destination for food lovers. Relax in a stylish cafe and dine with a view from more than a hundred restaurants, cafes and pubs, the dining scene just gets better and better. A taste of Nepali culture is still sought by tourists. Visitors are fascinated by the ethnic ambiance in local restaurants that serve authentic Nepali food.
Kathmandu has every kind of restaurant to satisfy the taste buds and palates of different types of people. You can find Thai, Mexican, Indian, Japanese, Australian, Russian, Korean, Italian, Chinese, Japanese, Tibetan, and Continental hangouts at par with the fast food joints, pubs to local restaurants which will serve you its authentic and sumptuous Nepali, Newari or Thakali food.
Please make sure that you have valid travel insurance to cover your time in the country. The organizers will not be held liable for illness, accidents, or thefts suffered by participants or accompanying persons during the conference or their stay in Nepal before or after the conference.
There are many buses, minibuses and micro-buses available at Ratnapark (Old Bus Park) which depart to different destinations in the valley. Three-wheelers that run on battery are also available for Kathmandu commuters.
Consult Kathmandu valley map to find out the direction of your destination. Hail a taxi, which is easily recognized by its taxi sign on top and black license plate. As a rough guide, a taxi will charge Rs. 30 per kilometer. No tip is expected. Private taxis may charge slightly higher. Night taxi services can also be arranged and operated by major hotels. Fare is slightly higher than a metered taxi. One can rent a private car through a travel agent or a car rental company.
The Sajha Yatayat has resumed bus services along two routes in the valley. It is currently operating along kalanki, kalimati, Tirpureshwor, Naya Banseshwor, Sinmangal and Airport and long Satdobato, Jawalakhel, Tripureshwor, Jamal, Teaching Hospital and Naya Bus Park. The buses are easily recognized by their green color and the name Sajha Yatayat on them.
Mountain bikes and ordinary bicycles are cheap and the best form of transportation for economy tourists. One can hire them at Thamel, Rani Pokhari, and Jhochhen, all in Kathmandu.
Long-distance day or night bus services are available from Kathmandu to all cities of Nepal. New Bus Park at Gongabu at Ring Road near Balaju, Kathmandu, from where buses depart to different destinations. Six seater Sumo Tata van, 12 seater van, and air-conditioned mini buses are also available for long-distance travel.
Nepal Airlines has an extensive network of air services to major parts of the country. Besides Nepal Airlines, other domestic airlines (there are more than 18 in operation) provide regular and chartered services to popular domestic destinations. [Source: Ministry of Culture, Tourism and Civil Aviation]
| Nepali Transliteration | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Namaste | Hello, Greetings, I bless the divine in you |
| Namaskar | The more respectful version of Namaste |
| Hajur | All-purpose term meaning yes? Pardon me, Excuse me? |
| (Tapaiilai) Kasto Cha? | How are you? |
| (Malai) Thik Cha | I am fine |
| Khana khannu bhaiyo? | Have you eaten? (used often as an informal greeting) |
| Dhanyabad | Thank you |
| Tapaiiko naam ke ho? | What is your name? |
| Mero naam Ann- Marie ho | My name is Ann-Marie |
| Maaph garnuhos | Excuse me/ pardon me/ sorry |
| Maile bhujhina | I don’t understand |
| Maile Bhujhe | I understand |
| Pheri bhetaunla | I hope we meet again |
| Tourist Police, Bhrikutimandap Tel:+977-1-4247041 |
Tourist Police, Thamel Tel:+977-1-4700750 |
| Tourist Police, Basantapur
Tel:+977-1-4268969,4269452 |
Tourist Police, Pokhara
Tel:+977-61-521087 |
|
Tourist Police, Belhiya
Tel:+977-71-520197 |
Police Headquarter Operation, Naxal
Tel:+977-1-4412780,4411549 |
|
Metro Police Control, Ranipokhari
Tel: 100, 120, 130 |
Department of Immigration, Kalikasthan
Tel:+977-1-4433934,4429660 |
|
Tourism Crisis Unit
Tel:+977-9751044088 |
Nepal Tourism Board, Bhrikutimandap
Tel:+977-1-4256909 |
|
Nepal Tourism Board, Pokhara
Tel: +977-61-465292,463029 |
Himalayan Rescue Association
Tel:+977-1-4440292,4440293 |
Every foreigner entering into presenting in trekking in or departing from Nepal shall in addition to the provisions laid down in the act and these rules uphold the following conduct and terms: